Fractal solar cells combine the principles of fractal geometry with photovoltaic technology, creating exciting possibilities for boosting energy efficiency through mathematically aesthetic designs. These panels are more efficient at capturing solar radiation than traditional solar panels, which are primarily flat and rectangular. Fractal geometry offers an alternative to traditional designs due to its self-similarity and complex patterns.
Understanding Fractal Geometry
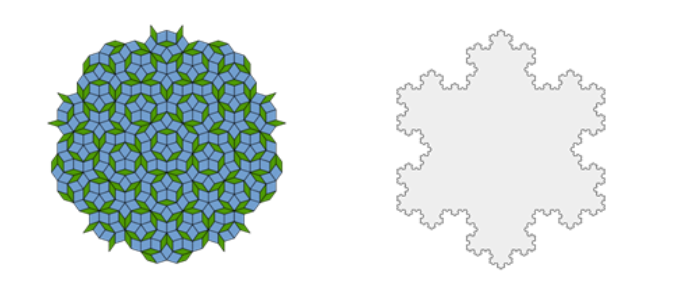
Fractals are mathematical constructs that exhibit self-similarity across all isotropic scaling. This means that the fractals retain their structural properties no matter the scale or which part of it is viewed. Meaning that a single fractal segment can represent the entire structure. Unlike standard geometric shapes that have whole-number dimensions, fractals have non-integer dimensions called the Hausdorff-Besicovitch dimensions [1]. Meaning that the set can take non-integer values in a way that it can effectively fill in spaces both quantitatively and qualitatively. The dimension is an index of complexity and a measure of how much space the pattern occupies. The idea of fractional dimension was brought to light by Mandelbrot [2]. These fascinating patterns are prevalent, appearing in forms like leaves, snowflakes, trees, lightning, lungs, galaxies, etc. Mathematical examples are Koch snowflakes, Sierpinski sets, Cantor sets, Mandelbrot sets, Julia sets, Penrose tiling, H-fractal, Pythagoras tree, etc.
Figure 1: Penrose tiling and Koch snowflakes [3], [4]
The Mathematical Modelling of Fractal Solar Cells
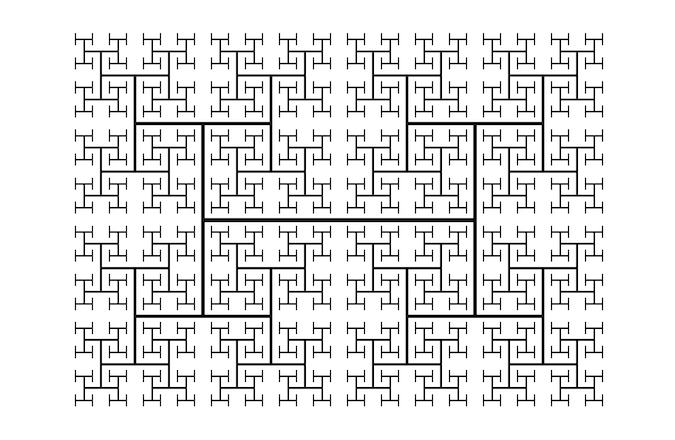
Fractal solar cells can be modelled mathematically to reflect their geometric characteristics. Researchers at the University of Oregon have created a hybrid design inspired by the fractal tree structure known as the ‘H-tree or H-fractal’ as shown in the Figure 2 below [5]. This design utilises perpendicular line segments, with each segment being smaller by a factor of the square root of two compared to the adjacent larger segment. Each canopy is formed by dividing a line segment into two smaller segments, which are then further divided, continuing this process infinitely. The H-tree creates a geometric shape that features a repeating pattern resembling the letter “H” and has a Hausdorff-Besicovitch dimension of two [6].
Figure 2: H-tree [7]
Efficiency and Applications of Fractal Solar Cells
The utilisation of fractal patterns in solar cells, instead of or in combination with busbar electrode designs, minimises photovoltaic material waste and maximises efficiency, ultimately reducing costs related to material production and installation. The fractal structure that more complex with each iteration, thereby increasing the effective surface area for capturing solar energy. The design emulates natural fractals, like the branching patterns found in trees. Fractal solar panels are capable of capturing light across various wavelengths and angles, allowing them to adapt to changing environmental conditions. This adaptability boosts their overall efficiency.
Researchers have designed a prototype solar panel inspired by fractal structures found in nature. Their research showed a 25% boost in overall energy output compared to conventional panels, along with omnidirectional performance [8].
Conclusion
The design of fractal solar cells makes them ideal for use in urban settings, such as on building facades and rooftops, where they can maximize energy capture in confined areas. Their lightweight and efficient characteristics can also improve the performance of portable solar devices. They mark a significant step forward in photovoltaic technology, combining the beauty and mathematical intricacies of fractals with energy collection systems.
About Pager Power
Pager Power undertakes technical assessments for developers of renewable energy projects and tall buildings worldwide. For more information about what we do, please get in touch.
References
[1] T. Gneiting, H. Ševčíková, and D. B. Percival, ‘Estimators of Fractal Dimension: Assessing the Roughness of Time Series and Spatial Data’, Stat. Sci., vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 247–277, May 2012, doi: 10.1214/11-STS370.
[2] B. B. Mandelbrot, The fractal geometry of nature, Revised edition. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman, 1982. Accessed: Oct. 15, 2024. [Online]. Available: http://catdir.loc.gov/catdir/bios/hol056/81015085.html
[3] Inductiveload, English: A Penrose tiling (P3) using thick and thin rhombi. Note the aperiodic structure, shared by all Penrose tilings. This particular Penrose tiling exhibits exact five-fold symmetry. 2009. Accessed: Oct. 15, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Penrose_Tiling_(Rhombi).svg
[4] Walwal20, English: 7th iteration of the Koch Snowflake. 2020. Accessed: Oct. 15, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koch_Snowflake_7th_iteration.png
[5] E. Roe et al., ‘Fractal solar panels: Optimizing aesthetic and electrical performances’, PLOS ONE, vol. 15, p. e0229945, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229945.
[6] V. Kaloshin and M. Saprykina, ‘An Example of a Nearly Integrable Hamiltonian System with a Trajectory Dense in a Set of Maximal Hausdorff Dimension’, Commun. Math. Phys., vol. 315, no. 3, pp. 643–697, Nov. 2012, doi: 10.1007/s00220-012-1532-x.
[7] Loopake, CC BY-SA 4.0, ‘H-tree’. Accessed: Oct. 15, 2024. [Online]. Available: <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
[8] Y. H. Sim, M. J. Yun, S. I. Cha, and D. Y. Lee, ‘Fractal solar cell array for enhanced energy production: applying rules underlying tree shape to photovoltaics’, Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., vol. 476, no. 2239, p. 20200094, Jul. 2020, doi: 10.1098/rspa.2020.0094.